Looking for the best method to keep your servers or high-performance computing systems cool? You are at the right place. Immersion cooling is the best solution to thermal problems. Let’s explore immersion cooling in-depth.
Table of Contents
What is Immersion Cooling?
It is a method used to cool electronic devices. These devices include high-performance computing systems and servers. They are submerged in a dielectric fluid that is thermally conductive but electrically insulating. Unlike traditional air cooling, it directly transfers heat from the electronic components to the cooling liquid. This method is highly effective in cooling high-performance computing systems and servers.
What is Dielectric Fluid?
Dielectric fluids are specially formulated liquids used in cooling systems to manage heat. They provide electrical insulation. Unlike other liquids like water, which conduct electricity and may harm electronic components, these fluids absorb and dissipate heat. They ensure optimal temperature ranges and improved system performance.
Properties:
Dielectric Fluids prevent short circuits and electrical failures. They efficiently transer heats from componensts. They remain stable under varying temperature consditions. They have low viscosity meaning that they circulate smootlhy and recuce energy comsumptionf for pumping reducign the operationcal costs.
Types:
There are several types of dielectric fluids, each with its own advantages and applications:
- Mineral Oils: Mineral oils are among the earliest types of dielectric fluids used for cooling. They are derived from petroleum and are relatively inexpensive. They are suitable for small-scale applications.
- Synthetic Fluids: Synthetic dielectric fluids are man-made and specifically engineered for cooling applications. They are used in high-performance computing systems and data centers.
- Fluorocarbons:Fluorocarbon-based dielectric fluids, such as those made from perfluorocarbons (PFCs), are known for their excellent cooling properties and low environmental impact. They are deal for sensitive and high-value equipment, such as supercomputers and quantum computers.
- Silicone Oils: Silicone oils are synthetic oils with a wide range of thermal stability and excellent electrical insulating properties. They are used in aerospace, military, and specialized industrial applications.
- Hydrocarbon-Based Fluids: These fluids are derived from hydrocarbons and are formulated to provide good thermal and electrical insulating properties. They are suitable for general-purpose cooling systems.
Working of Immersion Cooling
The basic principle of immersion cooling involves submerging the hardware in a special coolant. This coolant is thermally conductive and electrically insulating.
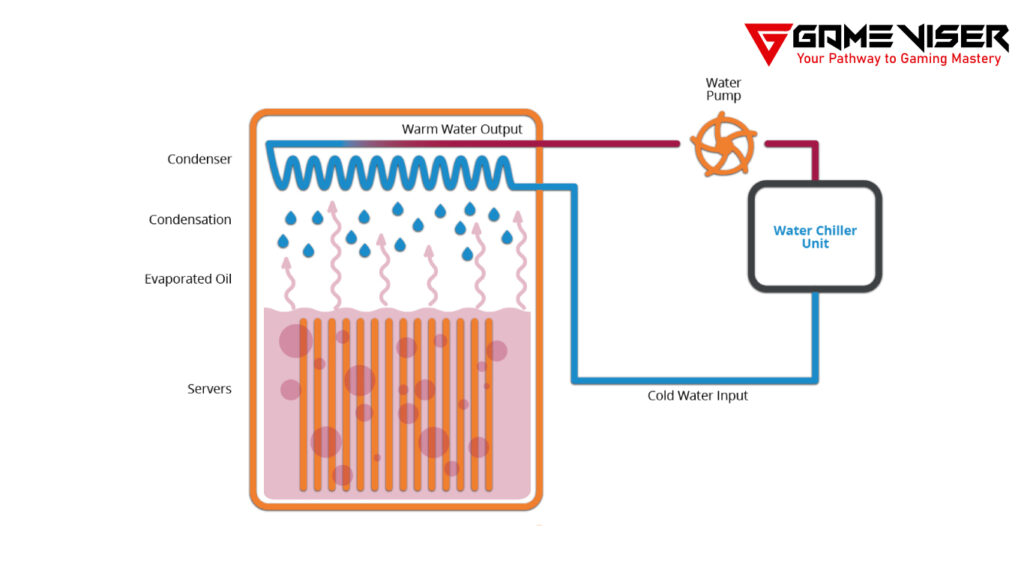
Firstly, electronic components, such as servers or GPUs, are fully submerged in a dielectric fluid. The electronic components do not get damaged as the fluid does not conduct electricity, as mentioned earlier. As the components operate, they generate heat. This heat is directly absorbed by the surrounding liquid. The liquid gets heated and now needs to be cooled down. For this purpose, the heated liquid is circulated through a cooling system, which includes heat exchangers or cooling towers. After passing through heat exchangers, the liquid is reinserted back into the tank.
Types of Immersion Cooling
Immersion cooling is of two types: Single-Phase and Two-Phase. They are explained below:
1. Single-Phase Immersion Cooling
In this method, the dielectric liquid absorbs heat and remains in the liquid state. The heated liquid is then pumped to a heat exchanger, where it is cooled and returned to the immersion tank.
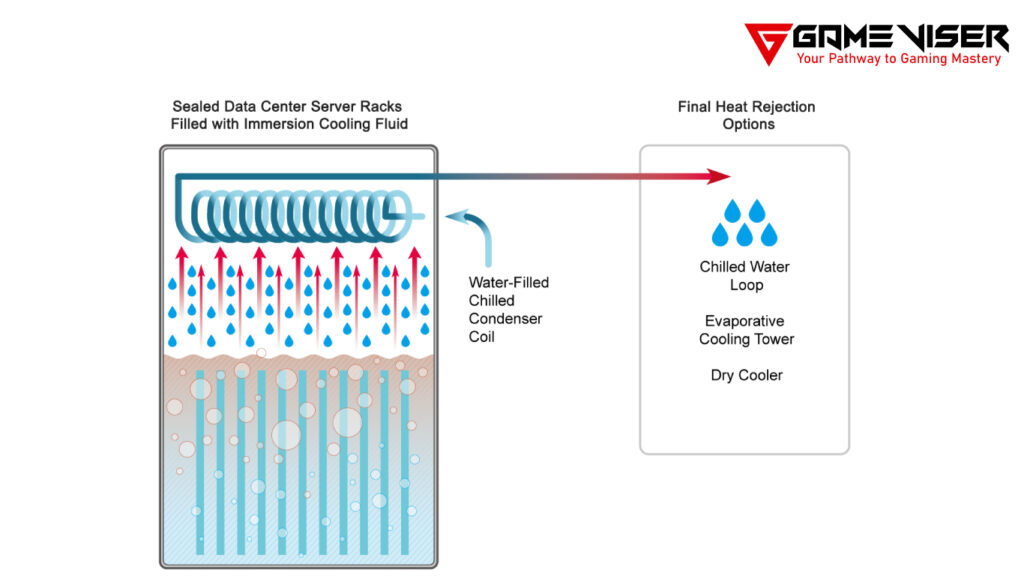
2. Two-Phase Immersion Cooling
Here, the dielectric fluid absorbs heat and changes from a liquid to a gas. The gas rises to the surface, where it condenses back into a liquid, releasing the heat in the process. The liquid then returns to the immersion tank by gravity.
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits of Immersion Cooling:
Direct contact between the cooling liquid and the hardware allows for improved heat transfer compared to air cooling.
It requires less energy, which reduces operational costs. One of the significant advantages of immersion cooling is that it reduces noise, as it does not need fans to operate.
When electronic components are operated in a well-managed thermal environment, their lifespan increases. In data centers, it also reduces the space required compared to air cooling systems.
In cryptocurrency mining, high heat is generated that needs to be controlled for optimal performance and improved lifespan of electronic components. Hence, immersion cooling proves to be one of the best solutions.
When it comes to supercomputing, such as in scientific research (HPC systems), quantum computing systems, and simulations, immersion cooling is the best solution to keep systems cool.
Challenges of Immersion Cooling:
One of the main challenges faced is its initial cost. The setup cost is higher compared to other cooling solutions. Moreover, the fluid requires careful handling and monitoring for maintenance. Integrating immersion cooling systems into existing infrastructure can be challenging.
Benchmark Results
Here’s a detailed table showing benchmark results for the average temperature achieved by different cooling methods in a high-performance computing environment:
| Cooling Method | Average Temperature (°C) | Minimum Temperature (°C) | Maximum Temperature (°C) | Temperature Range (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air Cooling | 45 | 40 | 50 | 10 |
| Single-Phase Immersion | 35 | 30 | 40 | 10 |
| Two-Phase Immersion | 30 | 25 | 35 | 10 |
| Liquid Cooling | 32 | 28 | 36 | 8 |
| Phase Change Cooling | 28 | 24 | 32 | 8 |
Here’s a sample table showing benchmark results for different cooling methods in a high-performance computing environment. This table includes hypothetical data including Average Temperature, Energy Consumpiotn, Cooling Efficiency and System Uptime, for comparison purposes.
| ooling Method | Average Temperature (°C) | Energy Consumption (kWh) | Cooling Efficiency (kW/°C) | System Uptime (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air Cooling | 45 | 1500 | 0.5 | 95 |
| Single-Phase Immersion | 35 | 1200 | 0.75 | 98 |
| Two-Phase Immersion | 30 | 1000 | 1.0 | 99 |
Future of Immersion Cooling
As technology advances and the demand for more efficient cooling solutions grows, immersion cooling is expected to become more widespread. Innovations in dielectric fluids and cooling system designs will continue to improve the feasibility and performance across various industries.

Conclusion
The technology is a revolutionary step in the cooling of electronic components. It offers enhanced efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and extended hardware lifespan. Although there are some challenges, its benefits are significant and it is a better option for data centers, cryptocurrency miners, and HPC systems.
FAQs
Is immersion cooling better than water cooling?
Yes, it is generally better than water cooling because it provides direct contact with cooling fluid and transfers heat in a better way.
What liquid is used for immersion cooling?
Dielectric fluids, such as mineral oils, synthetic fluids, fluorocarbons, silicone oils, and hydrocarbon-based fluids, are used due to their non-conductive properties.
Is immersion cooling expensive?
Yes, the initial setup costs are higher than those of other cooling solutions.
What are the risks of immersion cooling?
Risks include the initial high setup costs, the need for specialized maintenance, and potential issues with fluid handling and disposal. Proper safety protocols must be followed to prevent leaks and contamination.
What is 2-phase immersion cooling?
IThe dielectric fluid absorbs heat and changes from a liquid to a gas. The gas rises to the surface, where it condenses back into a liquid, releasing the heat in the process. The liquid then returns to the immersion tank by gravity.
What is the temperature of immersion cooling fluid?
The temperature typically ranges from 25°C to 50°C.




