Extended Reality (XR) is the umbrella term for immersive technologies like Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR). Let’s have a detailed look into the details of this technology and explore its applications in different industries.
Table of Contents
Introduction
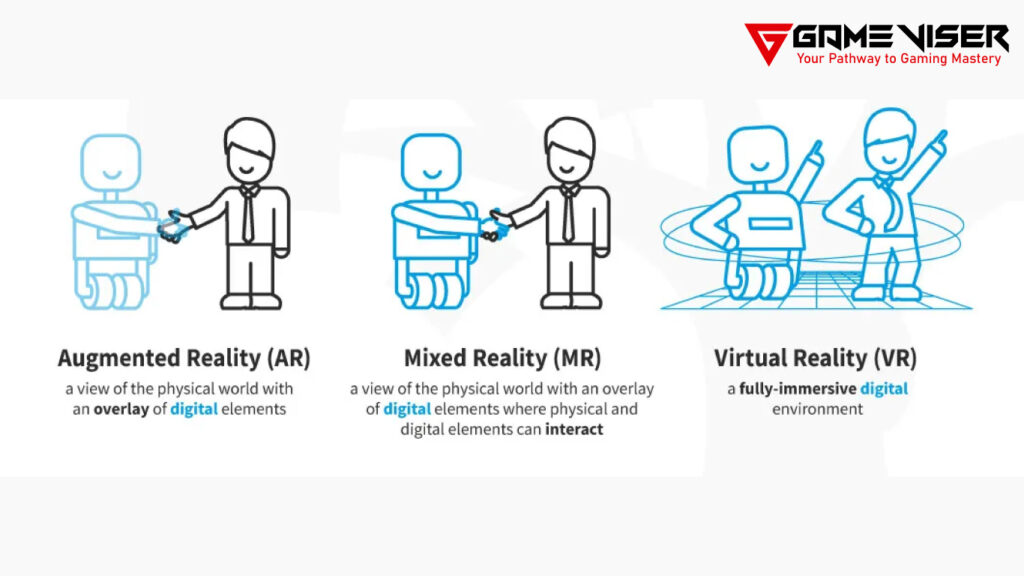
Extended Reality (XR) is the umbrella term that encompasses various technologies, including Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR). It is actually the combination of all these three technologies. Let’s first take a look at these three technologies and see what they are:
Virtual Reality (VR): It immerses users in a completely digital environment. Users can experience simulated worlds that feel lifelike through the use of VR headsets.
Augmented Reality (AR): It overlays digital elements onto the real world. Instead of replacing reality, AR enhances the world by adding virtual environments, objects, or information that are viewed through smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses.
Mixed Reality (MR): It combines VR and AR, enabling real-world objects and digital objects to interact in real-time. MR goes beyond simple overlays, allowing users to manipulate virtual objects within real-world settings.
Collectively, these technologies form the core of Extended Reality. (Read more about AR, VR, and MR)
Evolution
To understand the evolution of Extended Reality, we need to look back at the history of VR and AR in the 20th century. Early VR prototypes emerged in the 1960s and early 2000s. Advancements in computing power, display technology, and sensors led the technology to new heights, resulting in the invention of innovative solutions. AR gained significant attention with the launch of smartphone apps like Pokémon GO in 2016. The game surprised everyone by showcasing how digital content can blend with the physical world. The release of VR headsets like the Oculus Rift and HTC Vive elevated these technologies to new levels. Today, Extended Reality is no longer a futuristic concept; it is a rapidly growing industry with applications in gaming, healthcare, education, manufacturing, and more.

Required Components
The required components work together to create the experience of XR. These components include:
Displays and Headsets
VR headsets provide the ideal environments to experience Extended Reality. These headsets include the Meta Quest series and PlayStation VR, which are well-known devices at this time. Furthermore, AR glasses overlay information onto the physical world. These glasses include the Microsoft HoloLens 2 and Google Glass, among others.

Sensors and Tracking
Sensors track the user’s movements and position in real-time, allowing for accurate and precise interactions with digital elements. Cameras, gyroscopes, and accelerometers also play key roles, making the experience more natural and responsive.
3D Graphics and Content
Extended Reality environments rely heavily on high-quality 3D graphics generated in real-time. Game engines are used to create detailed XR content. Popular game engines like Unity and Unreal Engine are widely used in creating immersive XR content.
Input Devices
Hand controllers, gloves, and haptic feedback devices are used as input devices. These devices are far more advanced than ordinary keyboards and mice. They play a crucial role in enhancing XR experiences by allowing users to interact with virtual objects and receive tactile sensations through these input devices.

Cloud Computing and AI
Extended Reality experiences often require significant computational power, which is facilitated by cloud-based servers. Cloud computing reduces the processing load on local devices and makes XR more accessible. AI and machine learning algorithms are used to improve object recognition, scene understanding, and user interaction within XR environments.
Applications of Extended Reality (XR)
The versatility of XR technology has led to its adoption across a wide range of industries, including Gaming and Entertainment, Healthcare and Medical Training, Education and Training, Manufacturing and Design, Real Estate and Architecture, Retail and E-Commerce, Tourism and Hospitality, and more. Let’s explore the details:
Gaming and Entertainment
Gaming is one of the earliest and most prominent adopters of XR. VR games truly surprise players through immersive experiences, while AR-based games bring interactive experiences to the real world. The integration of XR in entertainment also extends to virtual concerts, theme parks, and 360-degree videos, among others.
Healthcare and Medical Training
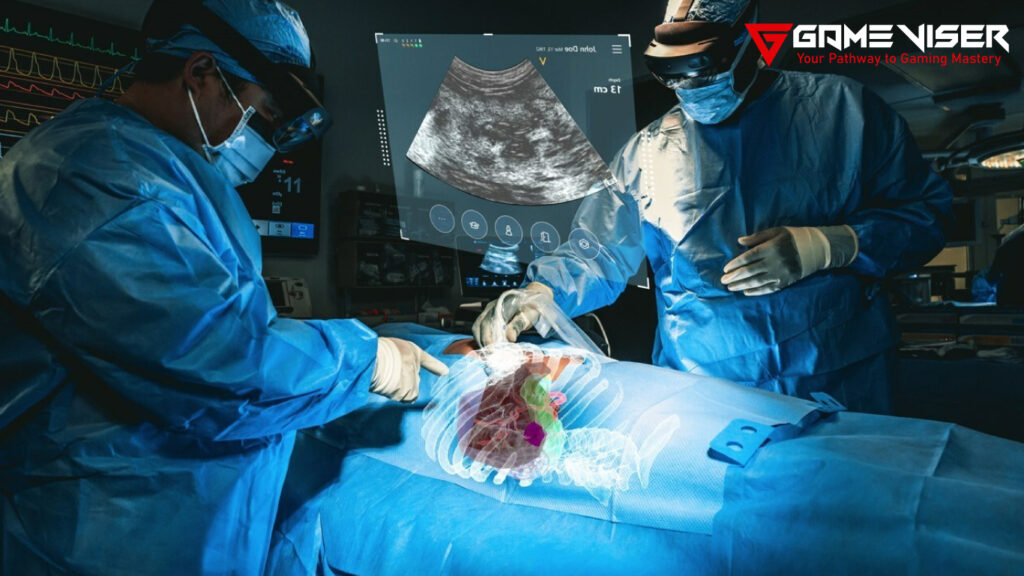
XR is revolutionizing the field of healthcare by improving medical training procedures and patient care processes. Medical professionals use VR simulations for surgical training, making complex procedures risk-free. AR is used to perform guided surgeries and display real-time information that assists surgeons during operations. Additionally, XR supports mental health therapies, rehabilitation, and pain management.
Education and Training
XR has improved learning experiences significantly. Virtual classrooms, historical reconstructions, and interactive science labs allow students to learn in engaging and interactive ways. In corporate training, XR is used to simulate real-life scenarios, helping employees acquire skills through experiential learning without associated risks or costs.
Manufacturing and Design
In the manufacturing sector, XR is used for design, prototyping, and quality control. Engineers and designers can visualize and interact with 3D models before building physical prototypes, reducing errors and speeding up development cycles. AR is also employed on factory floors to provide real-time information, assist workers with complex tasks, and enhance safety measures.
Real Estate and Architecture
Real estate professionals use XR to offer virtual property tours, allowing clients to explore homes remotely. Architects and interior designers use AR and VR to visualize building plans and design concepts at full scale, making it easier to identify potential issues and make adjustments early in the design process.
Retail and E-Commerce
XR is revolutionizing the retail experience by enabling customers to try products virtually before purchasing. AR apps allow users to see how furniture, clothing, or accessories will look in their homes or on their bodies.
Tourism and Hospitality
The tourism industry is leveraging XR to offer virtual travel experiences and interactive guides. Travelers can explore destinations, museums, and cultural landmarks from the comfort of their homes. Hotels and resorts are using VR to provide immersive previews of their accommodations and amenities.
Future of XR
The future of Extended Reality (XR) looks bright and promising. Advancements in VR, AR, MR, and XR technologies are leading to new innovations. The integration of 5G networks and edge computing will enhance XR capabilities by reducing latency and improving data processing speeds. This will result in more responsive and natural XR experiences, particularly in mobile and cloud-based applications.
As XR technology becomes more affordable, its adoption in enterprise settings will likely increase. XR is expected to involve greater interoperability between different platforms and devices, allowing users to transition more seamlessly between AR, VR, and MR environments. Developments in haptic feedback and sensory technologies, such as those for smell and taste, are being explored to make XR experiences more immersive and realistic.
Conclusion
Extended Reality (XR) has bridged the gap between the physical and virtual worlds. By combining AR, VR, and MR, XR provides a more immersive, natural, and realistic experience. As the technology becomes increasingly accessible and affordable, it is set to become an integral part of our daily lives.
FAQs
What is XR used for?
XR (Extended Reality) is used for immersive experiences in various fields, including gaming, training, education, healthcare, and entertainment.
What is XR vs AR?
XR (Extended Reality) is a broad term that includes AR (Augmented Reality), VR (Virtual Reality), and MR (Mixed Reality). AR overlays digital information on the real world, while XR encompasses all types of immersive technologies.
What is Extended Reality learning?
Extended Reality learning uses XR technologies to create immersive educational experiences, enhancing engagement and understanding through interactive simulations and virtual environments.
What are the three types of Extended Reality?
The three types are Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR).
What is an example of extended reality?
An example is a VR simulation that trains medical professionals in surgical procedures or AR apps that provide real-time information about landmarks.
What are the principles of extended reality?
The principles of XR include immersion, interaction, and contextualization, which focus on creating a seamless, engaging, and contextually relevant experience.