Looking to upgrade your PC? Check out the Top 7 Features To Look For in Your Next Motherboard, from chipset to future proofing your build.
Table of Contents
Introduction
When building or upgrading a PC, choosing the right motherboard is very important. It’s the backbone of your system, dictating what processors, memory, and other components you can use. Without the right motherboard, even the best CPU, GPU, or RAM may not perform at its full potential. But with so many options available, it can be hard to know which features really matter.
In this article, we’ll explore the top 7 features to look for in your next motherboard so that you can make an informed decision and build the perfect PC for your needs.
1. CPU Socket and Chipset Compatibility
The first thing you need to check when choosing a motherboard is whether it’s compatible with your chosen CPU. Motherboards are designed to work with specific CPU socket types and chipsets, which vary between Intel and AMD processors.
CPU Socket Types:
- Intel: Newer Intel processors (12th and 13th gen) use the LGA 1700 socket. Older CPUs like the 10th and 11th generations use the LGA 1200 socket.
- AMD: AMD Ryzen CPUs use the AM5 socket for newer generations, while AM4 is still used for older models.
Chipset Compatibility:
Along with the CPU socket, the motherboard’s chipset must be compatible with the processor. The chipset affects which features the motherboard can support, such as overclocking, the number of PCIe lanes, and the connectivity options.
For Intel, chipsets like Z790 or B760 are popular for high-end builds, while H610 caters to budget users. On the AMD side, chipsets like X670 and B650 are ideal for Ryzen processors.
2. Form Factor: ATX, Micro-ATX, or Mini-ITX
The size of the motherboard, known as the form factor, is another important consideration. The form factor determines how large or compact your build will be and what kind of case you can use.
Popular Motherboard Form Factors:
- ATX: The most common form factor, offering a good balance of features like multiple PCIe slots and memory slots. ATX motherboards are ideal for high-performance builds.
- Micro-ATX (mATX): Slightly smaller than ATX, Micro-ATX boards tend to offer fewer features but are more affordable. They fit into smaller cases while still offering decent expansion options.
- Mini-ITX: The smallest form factor, perfect for compact or portable builds. Mini-ITX boards come with limited ports and slots, so they are less expandable than larger options.
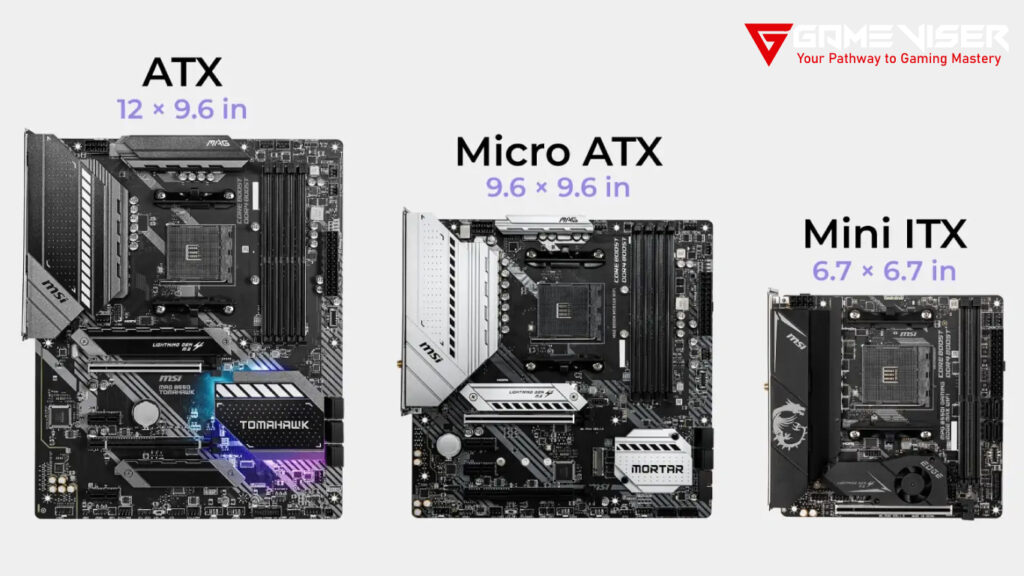
Here’s a table that differentiates ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX form factors:
| Feature | ATX | Micro-ATX (mATX) | Mini-ITX |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size | 12 x 9.6 inches (305 x 244 mm) | 9.6 x 9.6 inches (244 x 244 mm) | 6.7 x 6.7 inches (170 x 170 mm) |
| Expansion Slots | 7 expansion slots (for PCIe devices) | 4 expansion slots | 1 expansion slot |
| RAM Slots | Typically 4 (some high-end boards may have 8) | Typically 2-4 slots | 2 slots |
| Maximum RAM Support | Up to 128GB or more | Up to 128GB (varies) | Usually up to 64GB |
| SATA Ports | 6-8 ports (varies by board) | 4-6 ports | 2-4 ports |
| M.2 Slots | 1-3 (high-end boards may offer more) | 1-2 slots | Typically 1 slot |
| Ideal Use | High-performance builds, gaming, content creation | Mid-range builds, budget gaming | Compact builds, HTPC, portable systems |
| Power Phases | More power phases (better for overclocking) | Fewer power phases than ATX | Limited power phases (not ideal for overclocking) |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Mid-range pricing | Generally less expensive, but high-end boards can be costly |
| Case Compatibility | Requires standard ATX case | Compatible with ATX and mATX cases | Requires Mini-ITX or specific compact cases |
| Best For | Users needing maximum expandability and performance | Budget-conscious users with moderate expansion needs | Users seeking a small, compact build with limited expandability |
This table highlights the key differences between the form factors, helping users decide based on their specific needs, like size, expandability, and cost.
3. RAM Support: Number of Slots and Memory Speed
RAM is an essential component of any system, and your motherboard dictates how much memory you can install and at what speed. Modern applications and games are becoming more demanding, so having sufficient RAM is crucial for performance.
Key RAM Features to Consider:
- DIMM Slots: Most ATX motherboards come with 4 DIMM slots, allowing you to install up to 128GB or more of memory. Micro-ATX and Mini-ITX boards often have only 2 slots, limiting expansion.
- Maximum Memory Capacity: The motherboard sets the maximum amount of RAM your system can handle. High-end boards support up to 128GB or more, while budget boards might be limited to 64GB.
- Memory Speed: Make sure your motherboard supports fast RAM speeds, especially with DDR4 or DDR5 memory. Faster RAM speeds can significantly improve system performance, especially in gaming and content creation tasks.

Here’s a table highlighting the differences between DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5 RAM:
| Feature | DDR3 | DDR4 | DDR5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Release Year | 2007 | 2014 | 2020 |
| Data Rate (Speed) | 800 – 2133 MT/s | 1600 – 3200 MT/s | 4800 – 8400+ MT/s |
| Voltage | 1.5V | 1.2V | 1.1V |
| Bandwidth | 6.4 GB/s – 17 GB/s | 12.8 GB/s – 25.6 GB/s | 38.4 GB/s – 67.2 GB/s |
| Prefetch Buffer | 8-bit | 8-bit | 16-bit |
| Memory Channels | Dual Channel | Dual Channel | Dual Channel (but supports multi-threaded access) |
| Latency | CL9 – CL15 | CL15 – CL22 | CL30 – CL40 |
| Maximum Module Capacity | Up to 8 GB per module | Up to 64 GB per module | Up to 128 GB per module |
| Power Efficiency | Lower than DDR4 and DDR5 | Improved over DDR3 | Best power efficiency |
| ECC Support | Optional | Optional | Built-in on-die ECC (standard for DDR5) |
| Burst Length | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| Primary Usage | Older systems, budget builds | Mainstream and high-performance systems | High-performance, next-gen systems |
| Price | Lower (due to older tech) | Moderate (widely available) | Higher (newer tech) |
| Compatibility | Older motherboards (Intel 9th gen and earlier, AMD AM3) | Modern motherboards (Intel 6th to 11th gen, AMD AM4) | Latest motherboards (Intel 12th gen and newer, AMD AM5) |
This table provides a clear comparison between DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5 RAM, making it easier for users to decide which memory type is best for their system based on performance, efficiency, and compatibility.
4. Expansion Options: PCIe Slots and Connectivity
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slots are where you install additional components like graphics cards, sound cards, or storage expansion cards. The number and type of PCIe slots on your motherboard dictate how expandable your system will be.
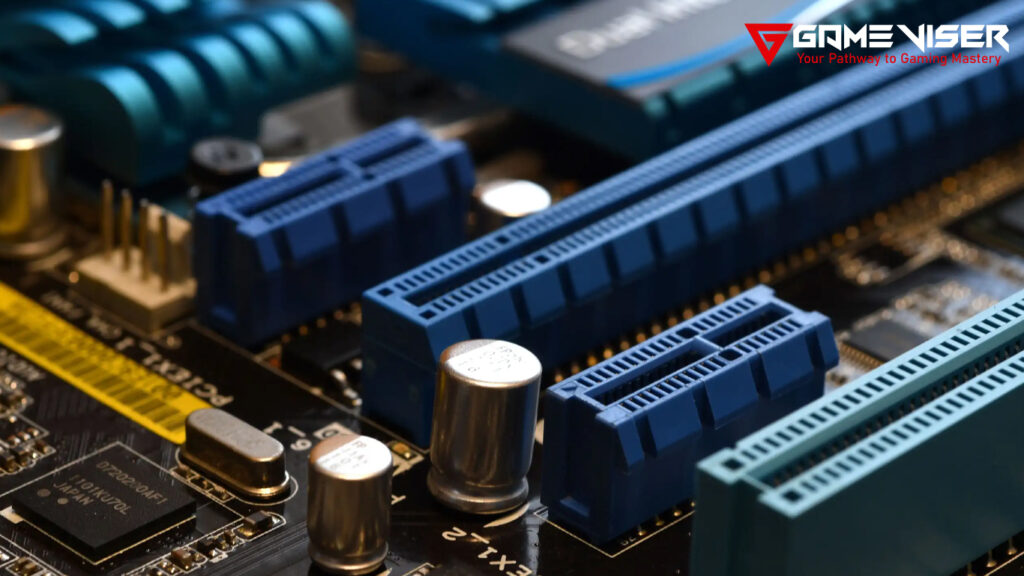
Key PCIe Slot Considerations:
- PCIe x16 Slot: If you plan to install a dedicated GPU, ensure the motherboard has at least one PCIe x16 slot. This is where high-performance graphics cards are installed.
- PCIe 4.0 and 5.0: PCIe 5.0 is the latest standard, offering double the bandwidth of PCIe 4.0. If you’re building a high-performance system, especially for gaming or content creation, ensure your motherboard has PCIe 4.0 or 5.0 slots.
- Multiple PCIe Slots: If you plan to run multiple GPUs or other PCIe-based devices, ensure the motherboard has more than one PCIe x16 slot. Multi-GPU setups (SLI or CrossFire) are less common now but still useful for specific workloads.
5. Storage Options: SATA, M.2, and NVMe Support
Storage is a critical component of any PC build, and your motherboard needs to offer enough connectivity for your storage devices. Modern motherboards come with various storage connection options.
Storage Features to Look For:
- SATA Ports: SATA is the standard interface for hard drives and older SSDs. Most motherboards come with 4-6 SATA ports, but some high-end boards may offer more.
- M.2 Slots: M.2 slots support newer NVMe SSDs, which are significantly faster than traditional SATA SSDs. Some motherboards offer multiple M.2 slots, allowing you to install more than one NVMe drive.
- RAID Support: Some motherboards allow you to set up RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations, which can improve data redundancy and performance.
6. USB Ports and External Connectivity
Modern PCs require a variety of connectivity options, from USB ports to network interfaces. The type and number of ports available on your motherboard will impact how many peripherals you can connect to your system.
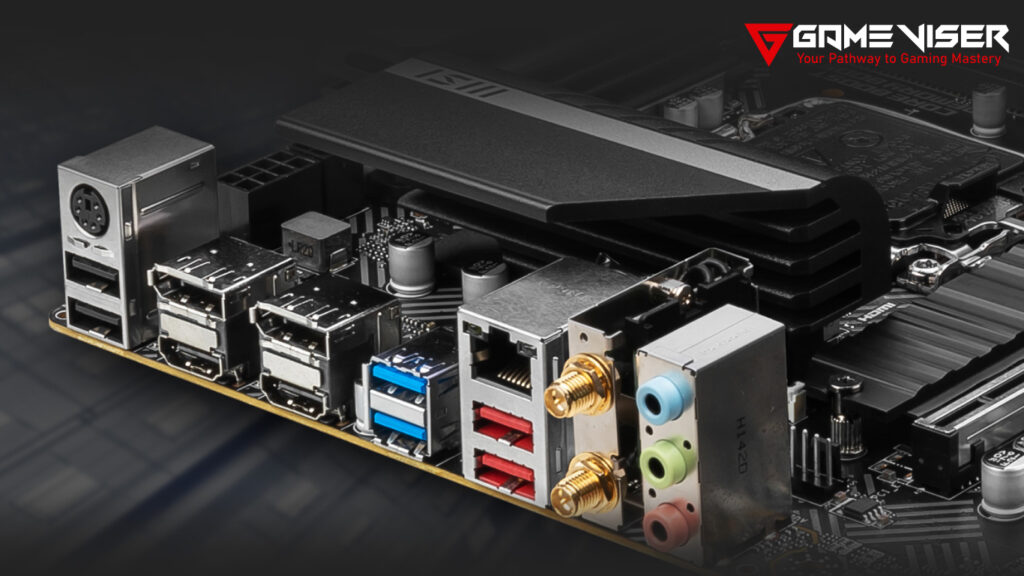

USB and Connectivity Features:
- USB 3.2 and 4.0: For fast data transfer speeds, prioritize motherboards with USB 3.2 or USB 4.0 ports. These offer much faster transfer rates than older USB standards.
- USB-C Ports: USB-C is becoming the universal standard for many devices, providing fast data transfer and power delivery. Some motherboards also support Thunderbolt 4 via USB-C, which is great for high-speed external storage or displays.
- Wi-Fi and Ethernet: Many modern motherboards come with built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, which is convenient if you don’t want to rely on an ethernet connection. Ensure the motherboard supports Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E for faster wireless speeds.
7. BIOS and Overclocking Features
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is the motherboard’s firmware that lets you control hardware settings, such as CPU, memory, and fan speed. For tech enthusiasts, having a motherboard with robust overclocking features is crucial to pushing the performance of your system.

BIOS and Overclocking Considerations:
- User-Friendly BIOS: Some motherboards come with more intuitive BIOS interfaces, making it easier to tweak settings and update firmware. Features like BIOS Flashback allow you to update the BIOS without needing a CPU installed.
- Overclocking Support: If you plan to overclock your CPU or memory, ensure the motherboard offers good power delivery and cooling options. Chipsets like Intel’s Z790 or AMD’s X670 are built with overclocking in mind.
- Automatic Tuning: Some motherboards come with automatic overclocking or performance tuning software, making it easier for beginners to boost their system performance without manual tweaking.
Conclusion
Selecting the right motherboard is essential for building a high-performance and future-proof PC. Whether you’re a gamer, content creator, or casual user, the motherboard plays a vital role in the overall system performance and upgradeability.
By focusing on these top 7 features, you’ll ensure that your next motherboard is not only compatible with your current components but also ready to support future upgrades. A well-chosen motherboard is a long-term investment that will serve you well, regardless of how technology evolves.
FAQs
What features should I look for in a motherboard?
Key features include chipset compatibility, form factor (ATX, Micro-ATX, Mini-ITX), number of PCIe slots, RAM support, storage options (SATA, M.2), power phases, and connectivity like USB ports and networking options.
What are the features of the motherboard?
A motherboard includes the CPU socket, RAM slots, PCIe expansion slots, storage connectors (SATA, M.2), power connectors, rear I/O ports (USB, audio), and cooling fan headers.
What are 4 things to think about when upgrading to a new motherboard?
Consider CPU compatibility, RAM type and capacity, expansion slots (PCIe for GPUs), and the form factor that fits your case.
What factors should be considered when choosing a motherboard?
Important factors include CPU compatibility, RAM support, expansion slots, storage options, power delivery, connectivity, and the form factor that fits your build.
How do I choose the right motherboard?
Choose based on your CPU, RAM, and expansion needs. Ensure it supports the components you want, fits your case, and has the right ports and slots for your peripherals.
What makes a motherboard better than another?
A better motherboard typically offers more expandability, better power delivery (for overclocking), more storage options (like M.2 slots), and advanced connectivity features like Wi-Fi 6 or Thunderbolt.